Getting Started¶
The OpenDev Workflow¶
The OpenDev workflow is centered around Gerrit, which uses the concept of changes rather than Pull Requests. To propose a change to a git repository, you start by cloning the repository you’re interested in, then create a branch to work in. You curate a commit on that branch, then propose it to Gerrit using the git-review tool:
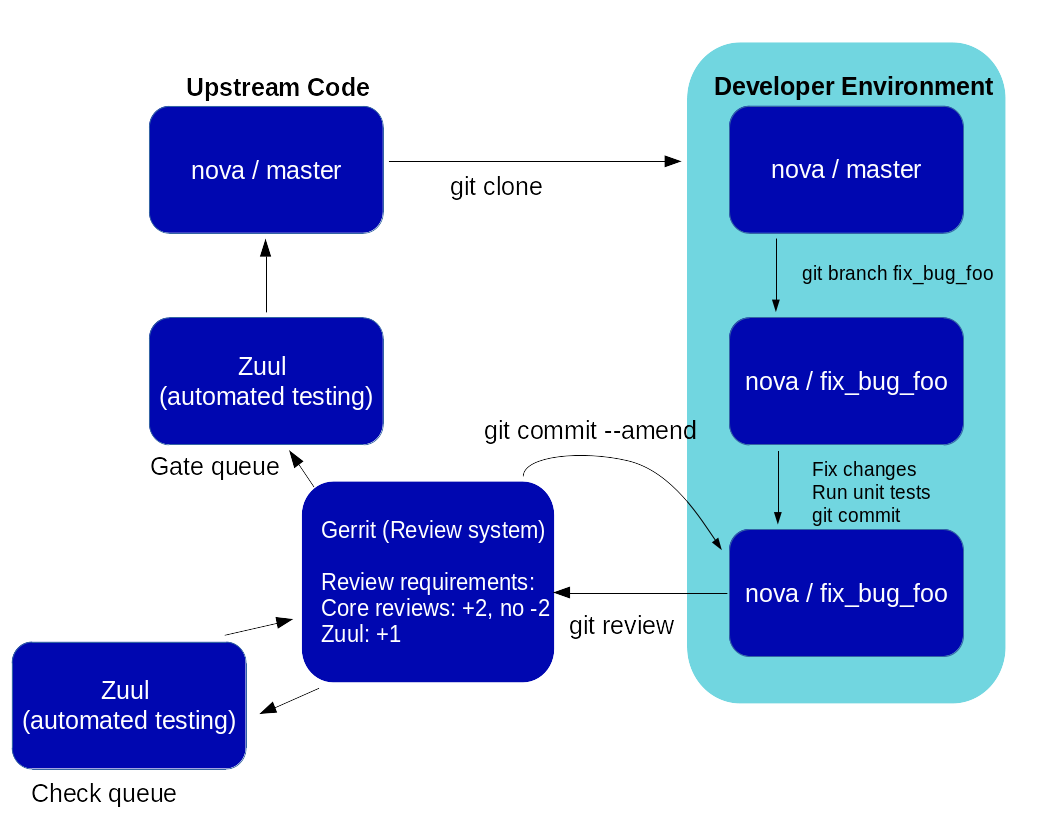
At that point, the proposed change is picked up by our Continuous Integration tool, Zuul, which runs check tests on it. The change is available for review by human reviewers. Those automated and human checks may result in you having to amend the proposed commit, then propose it again with git-review. Once the change is approved by both Zuul and the human reviewers, Zuul picks it up again and runs gate tests on it before finally merging it.
Setting up your Gerrit account¶
Get a single sign-on OpenID¶
Gerrit is currently using Ubuntu One as a SSO provider. You’ll therefore need a Ubuntu One account to use it. This account will also allow you to use Launchpad, which some projects on OpenDev use as a bug tracker.
Select a Gerrit username and upload your SSH key¶
Visit https://review.opendev.org/ and click the Sign In link
at the top-right corner of the page. Log in with your Ubuntu One
OpenID.
The first time you sign into OpenDev’s Gerrit site, you will be prompted to “Select a unique username:”. You can enter your Ubuntu One username here, or something else if you want. Type carefully, as once set it cannot be changed.
At that point you can already review proposed changes. To propose you own changes, you need to first upload your SSH key to Gerrit. This is done by visiting the SSH Public Keys section of your Gerrit settings.
Configure your local git environment¶
Ensure that you have run these steps to let git know about your email address:
git config --global user.name "Firstname Lastname"
git config --global user.email "your_email@youremail.com"
To check your git configuration:
git config --list
You’ll want to make sure that the user.email you specify matches
at least one you’ve provided to Gerrit. By default this is taken
from your OpenID login the first time you authenticate, but you can
also change it or add more addresses through the Contact
Information page
at any point in the future.
Install the git-review utility¶
git-review is a git subcommand tool that handles all the details of
working with Gerrit. You can learn more about git-review by reading its
documentation.
The git-review package is available on all major Linux distributions, so you can use your local package management tooling (apt-get, dnf, yum, zypper, pacman…) to install it directly. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu:
apt-get install git-review
On Mac OS X, or most other Unix-like systems, you may install it with pip:
pip install git-review
Git-review assumes that your Gerrit username is the same as the current running user on your operating system. If you are using different usernames and would like to avoid getting prompted, you should configure git to use your Gerrit username, as follows:
git config --global gitreview.username yourgerritusername
Proposing a change¶
Clone and prepare the git repository¶
Clone a repository in the usual way, for example:
git clone https://opendev.org/<namespace>/<projectname>
cd <projectname>
Then ask git-review to configure your repository to know about Gerrit:
git review -s
Feel free to check any unknown host key fingerprints against the Gerrit SSH Host Keys, and if you get an error about a missing contributor license agreement, see the Developer’s Guide section on the OpenStack Individual Contributor License Agreement.
Create a change in a topic branch¶
Create a topic branch to hold your work and switch to it:
git checkout -b TOPIC-BRANCH
Then modify files, and create a git commit as usual, for example using:
git commit -a
Submit a Change for Review¶
Now that your commit is ready, all you need to do is to send it to Gerrit for code review:
git review
Updating a Change¶
If the code review process suggests additional changes, make and amend the changes to the existing commit. Leave the existing Change-Id: footer in the commit message as-is, so that Gerrit knows this is an updated patchset for an existing change:
git commit -a --amend
git review
Next steps¶
We have a tutorial: Learn the Gerrit Workflow in the Sandbox. If this is your first time contributing to a project hosted by OpenDev, we strongly suggest you follow this tutorial.
You’ll find a lot more details about how to use Gerrit and Zuul in our Developer’s Guide.